The finance chiefs’ call comes amid a dispute over budget plans that the EU says go against Italy’s commitments to reduce its debt load. In an unprecedented rebuke, the European Commissionasked Italy last month to submit revised spending plans by Nov. 13, after it essentially rejected the country’s budget for 2019, saying that it constitutes a clear deviation from commonly agreed rules.

Giovanni Tria
But despite repeated warnings, Italian Finance Minister Giovanni Tria told reporters after the meeting in Brussels on Monday with his euro-area counterparts that the government would not change the budget law. The defiance means that even though Italy is willing to engage in talks with the commission over its spending plans, it’s unlikely to make sufficient concessions to appease Brussels.
“We expect a new and revised draft budgetary plan by Nov. 13 and that is a necessity,” EU economic affairs chief Pierre Moscovici told reporters after the meeting. “And the questions we have raised are still on the table.”
Better Explanations
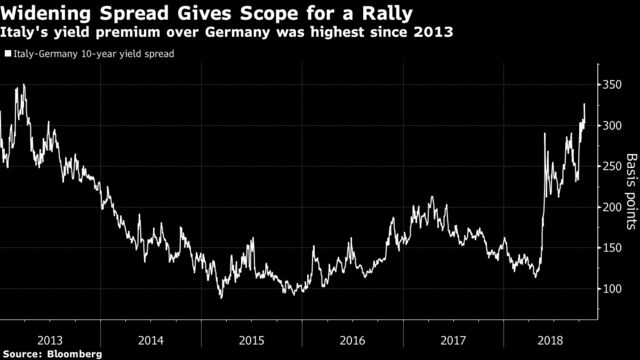
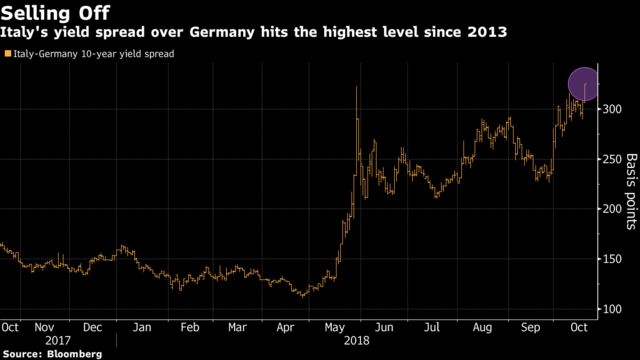
The commission’s call for a revised budget came after months of discord over the spending targets, which sent Italian bond yields to a four-year high last month.
But Tria also expressed optimism that Italian securities would recover. “We hope that the spread will go down when our strategy is better understood,” he said. “And maybe after the dialogue with the commission.”
During Monday’s meeting, the Italian finance chief told his colleagues that the country’s planned deviation was not huge and that EU rules allow for some flexibility, while he reiterated his government’s commitment to reduce the country’s debt load, an official familiar with the discussion said.
But Italy’s willingness to further explain the numbers and policies in the spending plans is unlikely to be enough to address the commission’s concerns.
In a joint statement, the bloc’s ministers said they agreed with the assessment by the commission and called on Italy to engage in “open and constructive dialogue” and to cooperate closely with the commission “in the preparation of a revised budgetary plan which is in line with the stability and growth pact.”
The statement also stressed the importance of sufficient debt reduction, a clear message to Italy, which has the highest debt ratio in the euro area after Greece.
‘Plan B’
Despite repeated warnings, Prime Minister Giuseppe Conte has said there’s no “Plan B” for the fiscal program, indicating the government has little intention to comply with EU demands.
Once Italy responds to the commission, the EU’s executive arm will have three weeks to publish its final assessment on whether the country’s spending plans are in breach of EU rules. One possible outcome, EU officials say, would be for the commission to bring up to Nov. 21 the publication of a report on Italy’s compliance with EU rules on debt that was originally planned for the spring.
EU Rules
If the report shows that Italy is failing to comply with rules on reducing its debt — which is more than twice the EU limit — then that could trigger the so-called excessive deficit procedure, a process that could eventually lead to financial sanctions for the government in Rome. The penalty could reach 0.2 percent of the country’s annual economic output, which was 1.7 trillion euros ($1.9 trillion) in 2017.
Euro-Area Finance Chiefs Talk Italy Amid Sanctions Threat
Financial penalties proposed by the commission have to be approved by member states, which can block the process. But while Brussels has limited powers over national budgets, governments have in the past sought to avoid an official reprimand because of the stigma and the potential market implications.
Under EU rules, no country should have a budget deficit larger than 3 percent of gross domestic product or debt above 60 percent of output and those that are outside of those limits must set annual targets to show they’re moving in the right direction. While Italy’s deficit is well within the 3 percent limit, the commission has demanded smaller gaps for the country to bring down its debt load.